Reflection and Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection and Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Refraction of Light, Absolute Refractive Index, Vertical Shift Due to Glass Slab & Refractive Index of a Glass Slab using a Travelling Microscope etc.
Important Questions on Reflection and Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Which of the following bearings and their uses are correct?
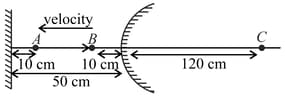
In the figure shown consider the first reflection at the plane mirror and second at the convex mirror. AB is object
When a monochromatic light ray is incident on a medium of refractive index with an angle of incidence , the angle of refraction is . If is changed slightly by , then the corresponding change in will be
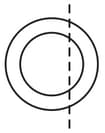
A spherical thick shell made of transparent material is cut along its chord as shown. The smaller part will
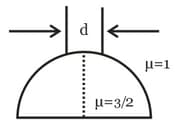
A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
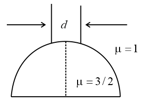
A beam of diameter is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to , then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two medium x & y 0f refractive index 4/3 & 3/2 respectively. If the object is placed along principal axis in medium X then
A vertical parallel beam of rays comes from bottom of a tank filled with a liquid. When it is accelerated with an acceleration of 7.5 m/s2, the ray is seen to be totally reflected by liquid surface. What is minimum possible refractive index of liquid?
A ray of light moving along the unit vector undergoes refraction at an interface of two media, which is the plane. The refractive index for is while for , it is . The unit vector along which the refracted ray moves is
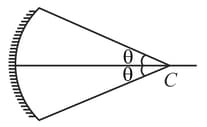
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle at its centre of curvature. The minimum value of for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principle axis suffers reflection more than one is
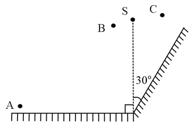
A point source of light is placed in front of two large mirrors as shown. Which of the following observers will see only one image of ?
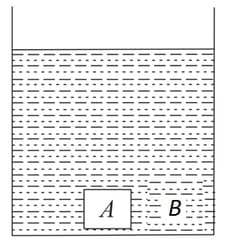
A parallel sided block of glass of refractive index which is thick rests on the floor of a tank which is filled with water (refractive index). The difference between the apparent depth of floor at and when seen from vertically above is equal to
A bird is flying 3 m above the surface of water. If the bird is diving vertically down with speed = 6 m/s, his apparent velocity as seen by a stationary fish underwater is:
A ray of sunlight enters a spherical water droplet () at an angle of incidence measured with respect to the normal to the surface. It is reflected from the back surface of the droplet and re-enters into the air. The angle between the incoming and outgoing ray is [Take ]
A point source of light is 60 cm from a screen and is kept at the focus of a concave mirror which reflects light on the screen. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. The ratio of average intensities of the illumination on the screen when the mirror is present and when the mirror is removed is:
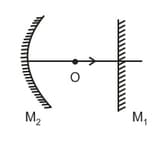
In the figure shown if the object 'O' moves towards the plane mirror, then the image I (which is formed after successive reflections from M1 & M2 respectively) will move:
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is:
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length . The near end of the rod is at a distance from the mirror. Its image will have a length
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
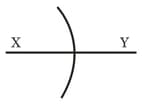
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

